Consider a solid
block of unit thickness for which the thermal conductivity decreases with an
increase in temperature. The opposite faces of the block are maintained at
constant but different temperatures: T(x = 0) > T(x = 1). Heat transfer is
by steady state conduction in x-direction only. There is no source or sink of
heat inside the block. In the figure below, identify the correct temperature
profile in the block.
(A)
I
(B)
II
(C)
III
(D)
IV
GATE
2015
Answer: (C)
Air is flowing
at a velocity of 3 m/s perpendicular to a long pipe as shown in the figure
below. The outer diameter of the pipe is d = 6 cm and temperature at the
outside surface of the pipe is maintained at 100°C. The temperature of the air
far from the tube is 30°C.
Data
for air: Kinematic viscosity, ν = 18×10-6 m2/s; thermal
conductivity, k = 0.03 W/(m.K)
Using
the Nusselt number correlation: Nu= hd/k = 0.024×Re0.8, the rate of
heat loss per unit length (W/m) from the pipe to air (up to one decimal place)
is _______________.
GATE
2015
Answer: 250 W/m
A heated solid
copper sphere (of surface area A and volume V) is immersed in a large body of
cold fluid. Assume the resistance to heat transfer inside the sphere to be
negligible and heat transfer coefficient (h), density (ρ), heat capacity (C),
and thermal conductivity (k) to be constant. Then, at time t, the temperature
difference between the sphere and the fluid is proportional to:
GATE 2015
Answer: (A)
In the figure
below, the temperature profiles of cold and hot fluids in counter current double
pipe heat exchangers (in different modes of operation) are shown on the left.
For each case, match the heat exchange process for the fluid represented by the
bold curve with the options given on the right.
(A)
I-P, II-Q, III-R, IV-S
(B)
I-P, II-Q, III-S, IV-R
(C) I-Q,
II-P, III-S, IV-R
(D) I-Q,
II-S, III-P, IV-R
GATE
2015
Answer: (C)
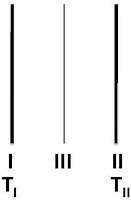
Two infinitely
large parallel plates (I and II) are held at temperature TI and TII
(TI > TII) respectively, and placed at a distance 2d
apart in vacuum. An infinitely large flat radiation shield (III) is placed in
parallel in between I and II. The emissivities of all the plates are equal. The
ratio of the steady state radiative heat fluxes with and without the shield is:
(A)
0.5
(B)
0.75
(C)
0.25
(D)
0
GATE
2015
Answer: (A)
Match
the dimensionless numbers in Group-1 with the ratios in Group-2
(A) P-II, Q-I, R-III
(B) P-I, Q-III, R-II
(C) P-III, Q-I, R-II
(D) P-II, Q-III, R-I
GATE 2016
Answer: (D)
Steam at 100oC is
condensing on a vertical steel plate. The condensate flow is laminar. The
average Nusselt numbers are Nu1 and Nu2, when the plate
temperatures are 10°C and 55°C, respectively. Assume the physical properties of
the fluid and steel to remain constant within the temperature range of
interest. Using Nusselt equations for film-type condensation, what is the value
of the ratio Nu2/Nu1?
(A)
0.5
(B)
0.84
(C)
1.19
(D)
1.41
GATE
2016
Answer: (C)
A composite wall is made of four
different materials of construction in the fashion shown below.
The resistance (in K/W) of each of
the sections of the wall is indicated in the diagram.
The
overall resistance (in K/W, rounded off to the first decimal place) of the
composite wall, in the direction of heat flow, is _______.
GATE
2016
Answer: 3.9 K/W
A jacketed
stirred tank with a provision for heat removal is used to mix sulphuric acid
and water ina steady state flow process. H2SO4 (l)
enters at a rate of 4 kg/h at 25oC and H2O (l)
enters at a rate of 6 kg/h at 10oC. The following data are
available:
Specific
heat capacity of water = 4.2 kJ kg‒1K‒1.
Specific
heat capacity of aqueous solution of 40 mass% H2SO4 = 2.8
kJ (kg solution)‒1 K‒1.
Assume the
specific heat capacities to be independent of temperature.
Based on reference states of H2SO4
(l) and H2 O (l) at 25oC, the heat of
mixing for aqueous solution of 40 mass% H2SO4 = ‒ 650 kJ
(kg H2SO4)‒1.
If the mixed
stream leaves at 40oC, what is the rate of heat removal (in kJ/h)?
(A)
1802
(B)
2558
(C)
5702
(D)
6458
GATE
2016
Answer: (A)
The
space between two hollow concentric spheres of radii 0.1 m and 0.2 m is under
vacuum. Exchange of radiation (uniform in all directions) occurs only between
the outer surface (S1) of the smaller sphere and the inner surface
(S2) of the larger sphere. The fraction (rounded off to the second
decimal place) of the radiation energy leaving S2, which reaches S1
is _______.
GATE
2016
Answer: 0.25
In an
experimental setup, mineral oil is filled in between the narrow gap of two
horizontal smooth plates. The setup has arrangements to maintain the plates at
desired uniform temperatures. At these temperatures, ONLY the radiative heat
flux is negligible. The thermal conductivity of the oil does not vary
perceptibly in this temperature range. Consider four experiments at steady
state under different experimental conditions, as shown in the figure below.
The figure shows plate temperatures and the heat fluxes in the vertical
direction.
What is
the steady state heat flux (in W m‒2) with the top plate at 70oC
and the bottom plate at 40oC?
(A)
26
(B)
39
(C)
42
(D)
63
GATE
2016
Answer: (A)
In
a 1- 1 pass shell and tube exchanger, steam is condensing in the shell side at
a temperature (Ts) of 135oC and the cold fluid is
heated from a temperature (T1) of 20oC to a
temperature (T2) of 90oC. The energy balance
equation for this heat exchanger is
Where U
is the overall heat transfer coefficient, A is the heat transfer area, m
is the mass flow rate of the cold fluid and cp is its
specific heat. Tube side fluid is in a turbulent flow and the heat
transfer coefficient can be
estimated from the following equation:
Nu = 0.023
(Re)0.8 (Pr)1/3
Where Nu
is the Nusselt number, Re is the Reynolds number and Pr is the Prandtl number.
The condensing heat transfer coefficient in the shell side is significantly
higher than the tube side heat transfer coefficient. The resistance of the wall
to heat transfer is negligible. If only the mass flow rate of the cold fluid is
doubled, what is the outlet temperature (in oC) of the cold fluid at
steady state?
(A)
80.2
(B)
84.2
(C)
87.4
(D) 88.6
GATE
2016
Answer: (B)
The
one dimensional unsteady heat conduction equation is
Where T - Temperature, t - time, r - radial position, k -
thermal conductivity, ρ-density, and Cp – specific heat.
For the cylindrical co-ordinate system, the value of n in the
above equation is
(A)
0
(B)
1
(C)
2
(D)
3
GATE 2017
Answer: (B)
In a heat exchanger, the inner dimeter of a tube is 25 mm and
its outer diameter is 30 mm. The overall heat transfer coefficient based on the
inner area is 360 W/m2°C. Then, the overall heat transfer
coefficient based on the outer area, rounded to the nearest integer, is
________ W/m2°C.
GATE
2017
Answer: 300
Let Ibλ be the spectral blackbody radiation
intensity per unit wavelength about the wavelength λ. The black body radiation
intensity emitted by a blackbody overall wavelength is
GATE
2017
Answer: (C)
A fluid flows over a heated horizontal plate maintained at
temperature Tw. The bulk temperature of the fluid is T∞. The temperature
profile in the thermal boundary layer is given by
Here, y is the vertical distance from the plate, δt
is the thickness of the thermal boundary layer and k is the thermal
conductivity of the fluid. The local heat transfer coefficient is given by
(A) k/2 δt
(B) k/δt
(C) 3k/2 δt
(D) 2k/ δt
GATE 2017
Answer: (C)
In nucleate boiling, the pressure inside a bubble is higher
than the pressure of the surrounding liquid. Assuming that both the liquid and
vapour are saturated, the temperature of the liquid will always be
(A) At 100°C
(B) Lower than the temperature of the vapour
(C) Equal to the temperature of the vapour
(D) Higher than the temperature of the vapour
GATE
2017
Answer: (B)