Bed pressure
drop in an air fluidized bed of catalyst particles (ρP = 2000 kg/m3,
Dp = 0.05 cm) of 60 cm bed depth and bed porosity of 0.5, expressed
in cm of water (manometer) is
(A)
90
(B)
60
(C)
45
(D)
30
(GATE 1995)
Answer: (B)
Air flows
through a packed bed of a powdery material of 1 cm depth at a superficial gas
velocity of 1 cm/s. A manometer connected to the unit registers a pressure drop
of 1 cm of water. The bed has a porosity of 0.4. Assuming that Kozeny-Carman
equation is valid for the range of study, estimate the particle size of the
powder. Ρair = 1.23 kg/m3, µair = 1.8×10-5
kg/m-s.
(A)
0.12 mm
(B)
0.14 mm
(C)
0.16 mm
(D)
0.18 mm
(GATE 1995)
Answer: (A)
A particle
attains its terminal settling velocity when
(A)
Gravity force + drag force = buoyancy
force
(B)
Gravity force - drag force = buoyancy
force
(C)
Buoyancy force + drag force = gravity
force
(D)
Drag force = buoyancy force
(GATE 1995)
Answer: (C)
Hydraulic mean
diameter for flow through packed bed of spherical particles of size dp
with porosity ε is
(GATE 1995)
Answer: (D)
A Newtonian
liquid (ρ = density, µ = viscosity) is flowing with velocity V in the tube of
diameter D. Let ΔP be the pressure drop across the length L. For a laminar
flow, ΔP is proportional to
(GATE 1994)
Answer: (C)
In fluidization
using perfect spherical particles, the operating range of fluidization velocity
is
(A)
Independent of particle size
(B)
Greater for bigger particle size
(C)
Greater for smaller particle size
(D)
Proportional to the square of particles
(GATE
1993)
Answer: (C)
For a
centrifugal pump, the net positive suction head (NPSH) is defined as
(A)
hvs + hps
(B)
hvd + hpd
(C)
hvs + hps-Ps
(D)
hvd + hpd-Pd
(GATE 1993)
Answer: (C)
A pitot tube
indicates 5 cm of water (manometer) when it is being used for measuring
velocity of air. The velocity of air in m/s is
(A)
5
(B)
14
(C)
56
(D)
26
(GATE 1992)
Answer: (D)
A spherical
particle is falling slowly in a viscous liquid such that Reynolds number is
less than 1, which statement is correct for this situation
(A)
Inertial and drag forces are important
(B)
Drag, gravitational and buoyancy forces
are important
(C)
Drag force and gravitational forces are
important
(D)
None of the above
(GATE 1992)
Answer: (B)
What size of
orifice would give a pressure difference of 41 cm water column for the flow of
liquid styrene of specific gravity 0.9 at 0.055 m3/s in a 250 mm
diameter pipe. Assume Cd = 0.62
(A)
181 mm
(B)
200 mm
(C)
210 mm
(D)
215 mm
(GATE 1991)
Answer: (A)
Bernoulli’s
equation for steady frictionless flow states that, along a stream line
(A)
Total pressure is constant
(B)
Total mechanical energy is constant
(C)
Velocity head constant
(D)
None of these
(GATE
1990)
Answer: (B)
For dilatant
fluid, the magnitude of slope of the shear stress versus the velocity gradient
curve …………. With increasing velocity gradient.
(A)
Increases
(B)
Decreases
(C)
Remains unchanged
(D)
May decrease or increase
(GATE 1989)
Answer: (A)
The condition
that is not necessary for the applicability of Bernoulli’s equation is
(A)
Steady state
(B)
Incompressible
(C)
Inviscid
(D)
Rotational
(GATE
1989)
Answer: (D)
The shear stress-shear
rate relationship for a liquid whose apparent viscosity decreases with
increasing shear rate is given by
(GATE 1989)
Answer: (A)
For an ideal
fluid flow, the Reynolds number is
(A)
Infinity
(B)
Zero
(C)
one
(D)
2100
(GATE 1988)
Answer: (A)
For pseudoplastic
fluids, increase in shear rate
(A)
Increases the apparent viscosity
(B)
Decreases the apparent viscosity
(C)
Has no effect on apparent viscosity
(D)
Has unspecified effect
(GATE 1988)
Answer: (A)
What pressure
drop per unit length is required in order to pump water at 25⁰C
through a pipe 5 cm in diameter at a velocity of 0.035 m/s and Re is 1700.
(A)
0.45 Pa/m
(B)
0.5 Pa/m
(C)
0.90 Pa/m
(D)
0.95 Pa/m
(GATE 1988)
Answer: (A)
Consider a duct
of square cross-section for side ‘b’, the hydraulic radius is given by
(A)
b/8
(B)
b/4
(C)
b/2
(D)
b
(GATE 1988)
Answer: (B)
For fluidized
bed, with increase in expansion of the bed, up to solids carryover from the
bed, the pressure drop across the bed
(A)
Increase rapidly
(B)
Decrease rapidly
(C)
First increases, then decreases
(D)
Remains essentially constant
(GATE 1988)
Answer: (D)
A liquid of
specific gravity 1.25 is drawing from the bottom of a large open tank through a
50 mm ID pipe. The drain pipe ends at a position 5 m below the surface of the
liquid in the tank. Calculate the velocity of flow at the point of discharge
from the pipe.
(A)
10.0 m/s
(B)
11.5 m/s
(C)
12.5 m/s
(D)
13.2 m/s
(GATE 1987)
Answer: (A)
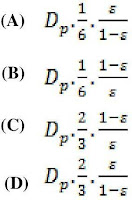


No comments:
Post a Comment