Losses
for flow through valves and fittings are expressed in terms of
(A)
Drag coefficient
(B)
equivalent length of a straight pipe
(C)
Shape factor
(D)
roughness factor
GATE
2008
Answer: (B)
Three
containers are filled with water up to the same height as shown. The pressures
at the bottom of the containers are denoted as P1, P2 and
P3. Which one of the following relationships is true?
(A)
P3>P1>P2
(B)
P2>P1>P3
(C)
P1>P2=P3
(D)
P1=P2=P3
GATE
2008
Answer: (D)
Given
a pipe of diameter D, the entrance length necessary to achieve fully developed
laminar flow is proportional to (NRe is Reynolds number)
GATE
2008
Answer: (A)
To
determine the performance of a compressor, a standardized test is performed. In
the testing process, when the compressor is under operation, “shut off” term
signifies
(A) Maximum
flow
(B) Zero
flow
(C) Steady
flow
(D) Intermittent
flow
GATE
2008
Answer: (B)
For
laminar flow conditions, the relationship between the pressure drop (ΔPc)
across an incompressible filter cake and the specific surface area (S0)
of the particles being filtered is given by one of the following
GATE
2008
Answer: (C)
The
power required for size reduction in crushing is
GATE
2008
Answer: (C)
A
cylindrical vessel with hemispherical ends is filled with water as shown in the
figure. The head space is pressurized to a gauge pressure of 40 kN/m2.
The vertical force F (in kN) tending to lift the top dome and the absolute
pressure P (in kN/m2) at the bottom of the vessel are
(g
= 9.8 m/s2, density of water = 1000 kg/m3)
(A)
F = 83.6; P = 64.5
(B)
F = 83.6; P = 165.8
(C)
F = 125.7; P = 64.5
(D)
F = 125.7; P = 165.8
GATE 2008
Answer: (C)
A
pump draws oil (specific gravity 0.8) from a storage tank and discharges it to
an overhead tank. The mechanical energy delivered by the pump to the fluid is
50 J/kg. The velocities at the suction and the discharge points of the pump are
1 m/s and 7 m/s, respectively. Neglecting friction losses and assuming kinetic
energy correction factor to be unity, the pressure developed by the pump (in
kN/m2) is
(A)
19.2
(B)
20.8
(C)
40
(D)
80
GATE
2008
Answer: (B)
Select
the most appropriate pump from Group 2 to handle each fluid flow given in Group
1.
Group 1 Group
2
P. Highly
viscous fluid flow 1.
Piston pump
Q. Fluid
containing large amount of abrasive solids 2.
Gear pump
3.
Plunger pump
4.
Centrifugal pump
(A)
P-2, Q-1
(B)
P-2, Q-4
(C)
P-3, Q-4
(D)
P-4, Q-3
GATE 2007
Answer: (B)
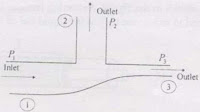
A pipeline
system carries crude oil of density 800 kg/m3. The volumetric flow
rate at point 1 is 0.28 m3/s. The cross sectional areas of the
branches 1, 2 and 3 are 0.012, 0.008 and 0.004 m2 respectively. All
the three branches are in a horizontal plane and the friction is negligible. If
the pressures at the points 1 and 3 are 270 kPa respectively, then the pressure
at point 2 is
(A)
202 kPa
(B)
240 kPa
(C)
284 kPa
(D)
355 kPa
GATE 2007
Answer: (C)
The figure shows
the idealized view of a return elbow or U bend, which is connected to two pipes
by flexible hoses that transmit no force. Water with density 1000 kg/m3
flows at velocity of 10 m/s through the pipe, which has a uniform ID of 0.1 m.
The gauge pressure at points 1 and 2 are 304 kPa and 253 kPa respectively. The
horizontal force F required to keep the elbow in position is
(A)
1574 N
(B)
1970 N
(C)
5942 N
(D)
7533 N
GATE
2007
Answer: (C)
A tube of
diameter D and length L is initially tilled with a liquid of density of ρ and
viscosity µ. It is then pushed out by the application of a constant force F to
the plunger as shown in the figure. Assuming laminar flow and pseudo steady
state, the time required to expel one half of the liquid out of the tube is
GATE 2007
Answer: (A)
The figure shows
a series-parallel configuration of three identical centrifugal pumps. The head
increase ΔH across a single such pump varies with flow rate Q according to ΔH=a
– bQ2. The expression for the total head increase ΔH = H2-H1
in terms of a and b and the total flow rate Q1 for this
configuration is given by
GATE 2007
Answer: (A)
The pressure
differential across a venture meter, inclined at 45⁰C to the vertical (as
shown in the figure) is measured with the help of a manometer to estimate the
flow rate of a fluid flowing through it. If the density of the flowing fluid is
ρ and the density of the manometer fluid is ρm, the velocity of the
fluid at the throat can be obtained from the expression
GATE 2007
Answer: (A)
In
the Stokes regime, the terminal velocity of particles for centrifugal
sedimentation is given by
Where, ω:
angular velocity; r: distance of the particle from the axis of rotation; ρp:
density of the particle; ρ: density of the fluid; dp: diameter of
the particle and µ: viscosity of the fluid.
In a bowl centrifugal classifier operating at 60 rpm
with water (µ = 0.001 kg/m.s), the time taken for a particle (dp =
0.0001 m, sp. Gr. = 2.5) in seconds to traverse a distance of 0.05 m from the
liquid surface is
(A)
4.8
(B)
5.8
(C)
6.8
(D)
7.8
GATE
2007
Answer: (C)
Common
statement for the next two questions
A
fluidized bed (0.5 m dia, 0.5 m high) of spherical particles (diameter = 2000
µm, specific gravity = 2.5) uses water as the medium. The porosity of the bed
is 0.4. The Ergun eqn for the system is
ΔP/L
(SI unit) at minimum fluidization condition is (g = 9.8 m/sec2)
(A)
900
(B)
8820
(C)
12400
(D)
17640
GATE 2007
Answer: (B)
The
minimum fluidization velocity (mm/sec) is
(A) 12.8
(B) 15.8
(C) 24.8
(D) 28.8
GATE 2007
Answer: (B)













No comments:
Post a Comment