The
height of a fluidized bed at incipient fluidization is 0.075 m, and the
corresponding voidage is 0.38. If the voidage of the bed increases to 0.5, then
the height of the bed would be
(A)
0.058 m
(B)
0.061 m
(C)
0.075 m
(D)
0.093 m
GATE
2010
Answer: (D)
A
storage vessel exposed to atmosphere (absolute pressure= 10.3 m of water) has a
diameter of 3 m and is initially filled with water to a height of 2 m. The pump
draws water from the vessel and is located at an elevation of 5 m above the
bottom of the vessel. The frictional head loss in the suction pipe is 2 m of
water. If the vapour pressure of the liquid at the temperature of operation is
3 m of water, then the available NPSH is
(A)
2.3 m
(B)
5.3 m
(C)
6.3 m
(D)
8.3 m
GATE
2010
Answer: (A)
In
Hagen-Poiseuille flow through a cylindrical tube, the radial profile of shear
stress is
(A)
Constant
(B)
Cubic
(C)
Parabolic
(D)
linear
GATE
2010
Answer: (D)
The stream function in
a xy-plane is given below
Ψ
= 1/2x2y3
The velocity vector for
this stream function is
GATE 2010
Answer: (B)
A hydrometer,
with stem cross-sectional area of 2.82×103 m2 is immersed
in a very large vessel containing water as shown in the figure. The immersed
volume is 15×10-6 m3 and the length of the stem above
water surface is Lw. If the entire volume of water is replaced by a
liquid with specific gravity 1.5 and if the length of the stem above the liquid
surface is Ll, then the difference, Ll - Lw is
(A)
-177 mm
(B)
177 mm
(C)
-266 mm
(D)
266 mm
GATE
2010
Answer: (B)
The diameter of
a drop of liquid fuel changes with time, due to combustion, according to the
relationship, D = D0(1-t/tb). While burning, the drop
falls at its terminal velocity under Stokes’ flow regime. The distance it will
travel before complete combustion, is given by
GATE
2010
Answer: (C)
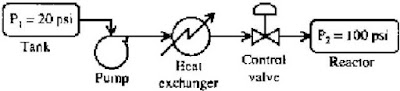
Consider the
process as shown below:
A
constant head pump transfers a liquid from a tank maintained at 20 psi to a
reactor operating at 100 psi, through a heat exchanger and a control valve. At
the design conditions, the liquid flow rate is 1000 litres/min, while the
pressure drop across that heat exchanger is 40 psi, and that across the control
valve is 20 psi. Assume that the pressure drop across the heat exchanger varies
as the square of the flow rate. If the flow is reduced to 500 litres/min, then
the pressure drop across the control valve is
(A)
30 psi
(B)
50 psi
(C)
80 psi
(D)
150 psi
GATE
2010
Answer: (B)
Under
fully turbulent flow conditions, the frictional pressure drop across a packed
bed varies with the superficial velocity (V) of the fluid as
(A)
V-1
(B)
V
(C)
V3/2
(D)
v2
GATE
2009
Answer: (D)
For
a mixing tank operating in the laminar regime, the power number varies with the
Reynolds number (Re) as
(A)
Re-1/2
(B)
Re1/2
(C)
Re
(D)
Re-1
GATE
2009
Answer: (D)
Two
identical reservoirs, open at the top, are drained through pipes attached to
the bottom of the tanks as shown below. The two drain pipes are of the same
length, but of different diameters (D1>D2)
Assuming
the flow to be steady and laminar in both drain pipes, if the volumetric flow
rate in the larger pipe is 16 times of that in the smaller pipe, the ratio D1/D2
is
(A)
2
(B)
4
(C)
8
(D)
16
GATE
2009
Answer: (A)
For
an incompressible flow, the x- and y- components of the velocity vector are
Vx = 2(x + y); vy
= 3(y + z)
Where
x, y, z are in meters and velocities are in m/s. Then the z-component of the
velocity vector (vz) of the flow for the boundary condition vz
= 0 at z = 0 is
(A)
5z
(B)
-5z
(C)
2x + 3z
(D)
-2x-3z
GATE 2009
Answer: (B)
The terminal
settling velocity of a 6 mm diameter glass sphere (density: 2500 kg/m3)
in a viscous Newtonian liquid (density: 1500 kg/m3) is 100 µm/s. If
the particle Reynolds number is small and the value of acceleration due to
gravity is 9.81 m/s2, then the viscosity of the liquid (in Pa.s) is
(A)
100
(B)
196.2
(C)
245.3
(D)
490.5
GATE
2009
Answer: (B)
Match
the equipment in group I to the internals in Group II
Group
I Group
II
P.
Centrifugal pump 1.
Baffle
Q.
Distillation column 2.
Impeller
R.
Heat exchanger 3.
Tray
4.
Volute
(A)
P-2, Q-1, R-4
(B)
P-2, Q-4, R-3
(C)
P-1, Q-3, R-4
(D)
P-4, Q-3, R-1
GATE
2009
Answer: (D)
Common
statement for the next two questions
A free jet of water is emerging from a
nozzle (diameter 75 mm) attached to a pipe (diameter 225 mm) as shown below.
The velocity of water at point A is 18
m/s. Neglect friction in the pipe and nozzle. Use g = 9.81 m/s2 and
density of water = 1000 kg/m3.
The velocity of water at the tip of the
nozzle (in m/s) is
(A) 13.4
(B) 18.0
(C) 23.2
(D) 27.1
GATE
2009
Answer: (D)
The gauge pressure (in kPa) at point B
is
(A) 80.0
(B) 100.0
(C) 239.3
(D) 367.6
GATE
2009
Answer: (D)






No comments:
Post a Comment