According
to the penetration theory of mass transfer, the mass transfer coefficient (k)
varies with diffusion coefficient (D) of the diffusing species as
(A)
D
(B)
D-1/2
(C)
D1/2
(D)
D3/2
GATE
2009
Answer: (C)
The
ratio of the liquid to gas flow rate in a counter-current gas absorption column
is increased, at otherwise identical conditions. Which one of the following
statements is true?
(A)
The operating line shifts towards the
equilibrium curve
(B)
The operating line shifts away from the
equilibrium curve
(C)
The concentration of the absorbed
species increases in the exit liquid stream
(D)
The operating line does not shift
GATE
2009
Answer: (B)
Species A is diffusing at steady state
from the surface of a sphere (radius = 1 cm) into a stagnant fluid. If the
diffusive flux at a distance r = 3 cm from the center of the sphere is 27
mol/cm2.s, the diffusive flux (in mol/cm2.s) at a
distance r = 9 cm is
(A)
1
(B)
3
(C)
9
(D)
27
GATE 2009
Answer: (B)
The feed to a
binary distillation column has 40 mol % vapour and 60 mol % liquid. Then, the
slope of the q-line in the McCabe-Thiele plot is
(A)
-1.5
(B)
-0.6
(C)
0.6
(D)
1.5
GATE
2009
Answer: (A)
The equilibrium moisture curve for a
solid is shown below:
The total moisture content of the solid
is X and it is exposed to air of relative humidity H. In the table below, Group
I lists of the type of moisture, and Group II represents the region in the
graph above
|
Group
I |
Group
II |
|
P. Equilibrium moisture |
1 |
|
Q. Bound moisture |
2 |
|
R. Unbound moisture |
3 |
|
S. Free moisture |
4 |
Which one of the following is the
correct match?
(A)
P-I, Q-2, R-3, S-4
(B)
P-I, Q-3, R-4, S-2
(C)
P-I, Q-4, R-2, S-3
(D)
P-I, Q-2, R-4, S-3
GATE
2009
Answer: (B)
An
equimolar mixture of four hydrocarbons (1, 2, 3, 4) is to be separated into
high purity individual components using a sequence of simple distillation
columns (one overhead and one bottom stream). Four possible schemes are shown
below.
|
Component |
Ki |
|
1 |
6 |
|
2 |
3 |
|
3 |
2.5 |
|
4 |
1.1 |
Using
the Ki (= yi*/xi) values given above,
the optimal scheme is
(A)
P
(B)
Q
(C)
R
(D)
S
GATE 2009
Answer: (D)
Common
data for the next two questions
A flash distillation drum (see figure below) is used to separate a methanol –water mixture. The mole fraction of methanol in the feed is 0.5, and the feed flow rate is 1000 kmol/hr. The feed is preheated in a heater with heat duty Qh and is subsequently flashed in the drum. The flash drum can be assumed to be an equilibrium stage, operating adiabatically. The equilibrium relation between the mole fractions of methanol in the vapour and liquid phases is y* = 4x. The ratio of distillate to feed flow rate is 0.5.
The mole fraction of methanol in the
distillate is
(A) 0.2
(B) 0.7
(C) 0.8
(D) 0.9
GATE 2009
Answer: (C)
If the enthalpy of the distillate with
reference to the feed is 3000 kJ/kmol, and the enthalpy of the bottoms with
reference to the feed is -1000 kJ/kmol, the heat duty of the preheater (Qh
in kJ/hr) is
(A) -2×106
(B) -1×106
(C) 1×106
(D) 2×106
GATE 2009
Answer: (C)
For
a system containing species P, Q and R, composition at point k on the ternary
plot is
(A)
62.5% P, 12.5% Q, 25% R
(B)
25% P, 62.5% Q, 12.5% R
(C) 12.5% P, 62.5% Q, 25% R
(D) 12.5% P, 25% Q, 62.5% R
GATE
2008
Answer: (A)
In
a countercurrent gas absorber, both the operating and equilibrium relations are
linear. The inlet liquid composition and the exit gas composition are
maintained constant. In order to increase the absorption factor
(A)
The liquid flow rate should decrease
(B)
The gas flow rate should increase
(C)
The slope of the equilibrium line should
increase
(D)
The slope of the equilibrium line should
decrease
GATE
2008
Answer: (D)
A
rectangular slab of thickness 2b along the x axis and extending to infinity
along the other directions is initially at concentration CA0. At
time t = 0, both surfaces of the slab (x = ±b) have their concentrations
increased to CAW and maintained at that value. Solute A diffuses
into the solid. the dimensionless concentration C is defined as
C = (CA-CA0)/(CAW
– CA0)
The
diffusivity of A inside the solid is assumed constant. At a certain time
instant, which one of the following is the correct representation of the
concentration profile?
GATE
2008
Answer: (C)
In
a binary mixture containing components A and B, the relative volatility of A
with respect to B is 2.5 when mole fractions are used. The molecular weights of
A and B are 78 and 92 respectively. If the compositions are however expressed
in mass fractions the relative volatility will then be
(A)
1.18
(B)
2.12
(C)
2.5
(D)
2.95
GATE 2008
Answer: (C)
An
ideal flash vaporization is carried out with a binary mixture at constant
temperature and pressure. A process upset leads to an increase in the mole
fraction of the heavy component in the feed. The flash vessel continues to
operate at the previous temperature and pressure and still produces liquid and
vapour. After steady state is re-established,
(A)
The amount of vapour produced will
increase
(B)
The amount of liquid produces will
decrease
(C)
The new equilibrium compositions of the
vapour and liquid products will be different
(D)
The new equilibrium compositions of the
vapour and liquid products will remain as they were before the upset occurred
GATE 2008
Answer: (D)
A batch distillation operation is carried out to separate a feed containing 100 moles of a binary mixture of A and B. The mole fraction of A in the feed is 0.7. The distillation progress until the mole fraction of A in the residue decreases to 0.6. The equilibrium curve in this composition range may be linearized to y* = 0.7353x + 0.3088. Here x and y are the mole fractions of the more volatile component A in the liquid and vapour phases respectively. The number of moles of residue is
(A)
73.53
(B)
48.02
(C)
40
(D)
30.24
GATE
2008
Answer: (B)
A
packed tower containing Berl saddles is operated with a gas-liquid system in
the countercurrent mode. Keeping the gas flow rate constant, if the liquid flow
rate is continuously increased,
(A)
The void fraction available for the gas
to flow will decrease beyond the loading point
(B)
The gas pressure drop will decrease
(C)
Liquid will continue to flow freely down
the tower beyond the loading point
(D)
The entrainment of liquid in the gas
will considerably decrease near the flooding point
GATE 2008
Answer: (A)
A
sparingly soluble solute in the form of a circular disk is dissolved in an
organic solvent as shown in the figure. The area available for mass transfer
from the disk is A and the volume of the initially pure organic solvent is V.
The disk is rotated along the horizontal plane at a fixed rpm to produce a
uniform concentration of the dissolving solute in the liquid.
The convective mass transfer coefficient
under these conditions is kc. The equilibrium concentration of the
solute in the solvent is C*. The time required for the concentration
to reach 1% of the saturation value is given by
GATE
2008
Answer: (A)
Air
concentrated with solute P is brought in contact with water. At steady state,
the bulk concentrations of P in air and water are 0.3 and 0.02 respectively.
The equilibrium equation relating the interface compositions is
yP,i =
0.25xP,i
Assume
that the mass transfer coefficients FG and FL are
identical. The gas phase mole fraction of P at the interface (yP,i)
is
(A)
0.0663
(B)
0.075
(C)
0.16
(D)
0.3
GATE
2008
Answer: (A)
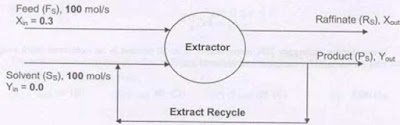
A
feed (F) containing a solute is contacted with a solvent (S) in an ideal stage
as shown in the diagram below. Only the solute transfer into the solvent. The
flow rates of all the streams are shown on a solute free basis and indicated by
the subscript S. The compositions of the streams are expressed on a mole ratio
basis. The extract leaving the contactor is divided into two equal parts, one
part collected as the product (P) and the other stream is recycled to join the
solvent. The equilibrium relationship is
Y* =
2X
The
product flow rate (Ps) and composition (Yout) are
(A)
Ps = 50 mol/s, Yout
= 0.3
(B)
Ps = 100 mol/s, Yout
= 0.2
(C)
Ps = 200 mol/s, Yout
= 0.1
(D)
Ps = 100 mol/s, Yout
= 0.4
GATE
2008
Answer: (B)
Common statement for the next two questions
A
thin liquid film flows at steady state along a vertical surface as shown in the
figure. The average velocity of the liquid film is 0.05 m/s. The viscosity of
the liquid is 1 cP and its density is 1000 kg/m3. The initially pure
liquid absorbs a sparingly soluble gas from air as it flows down. The length of
the wall is 2 m and its width is 0.5 m. The solubility of the gas in the liquid
is 3.4×10-2 kmol/m3 and isothermal conditions may be
assumed.
If
the exit average concentration in the liquid is measured to be 1.4×10-2
kmol/m3, the total mass transfer rate (in kmol/s) of the sparingly
soluble gas into the liquid is
(A) 0.133×10-4
(B) 0.434×10-7
(C) 3.4×10-2
(D) 17×10-2
GATE 2008
Answer: (B)
The
mass transfer coefficient kc,avg (in m/s), averaged along the length
of the vertical surface is
(A) 2.94×10-6
(B) 2.27×10-6
(C) 1.94×10-6
(D) 1.65×10-6
GATE 2008
Answer: (D)








No comments:
Post a Comment