An
equimolar mixture of A and B (A being more volatile) is flash distilled continuously
at a feed rate of 100 kmol/h, such that the liquid product contains 40 mol% of
A. If the relative volatility is 6, then the vapour product in kmol/h is
(A)
10
(B)
20
(C)
25
(D)
45
GATE 2012
Answer: (C)
Consider
the drying operation shown in the figure below for a solid loading (dry basis)
of 50 kg/m2 with a constant drying rate of 5 kg/m2.h. The
falling rate of drying is linear with moisture content.
The
drying time in hours required to reduce an initial moisture content of 25% to a
final moisture content of 2% is
(A)
1.55
(B)
1.75
(C)
3.25
(D)
4.55
GATE
2012
Answer: (C)
In
the Mc-Cabe-thiele diagram, if the x-coordinate of the point of intersection of
the q-line and the vapour-liquid equilibrium curve is greater than the
x-coordinate of the feed point, then the quality of the feed is
(A)
Superheated vapour
(B)
Liquid below bubble point
(C)
Saturated vapour
(D)
Saturated liquid
GATE
2012
Answer: (B)
For
which of the following combinations, does the absorption operation become
gas-film controlled?
(P) The
solubility of gas in the liquid is very high
(Q) The
solubility of gas in the liquid is very low
(R) The
liquid-side mass transfer coefficient is much higher than the gas-side mass
transfer coefficient
(S) The
liquid-side mass transfer coefficient is much lower than the gas-side mass
transfer coefficient
(A)
P & Q
(B)
P & R
(C)
P & S
(D)
Q & R
GATE
2012
Answer: (B)
Common
data for the next two questions
A
counter-current extraction column is designed to remove 99% of solute C from a
solution of solvent A and solute C using pure solvent B. the initial
concentration of solute in the solution of A + C is 20 wt%, and the total flow
of solution is 1000 kg/h. If the equilibrium relationship is Y = 2X, where Y =
mass of C/mass of A and X = mass of C/mass of B.
The minimum flow rate of solvent B
required in kg/h is
(A)
1454
(B)
1584
(C)
1676
(D)
1874
GATE 2012
Answer: (B)
If the flow rate of B is 2400 kg/h,
then the theoretical number of stages in the column, using Kremser’s equation
adjusted to the next integer is
(A)
5
(B)
9
(C)
11
(D)
13
GATE 2012
Answer: (B)
Common Data for the next two
questions
A
binary feed mixture containing equimolar quantities of components S and T is to
be distilled in a fractionating tower at atmospheric pressure. The distillate
contains 96 mol % S. The q-line (feed line) intersects the equilibrium line at
x' = 0.46 and y'= 0.66, where x' and y' are mole fractions. Assume that the
McCabe-Thiele method is applicable and the relative volatility is constant.
The
minimum reflux ratio is
(A) 1.6
(B) 1.5
(C) 0.66
(D) 0.6
GATE
2011
Answer: (B)
The
feed is
(A) At dew point
(B) At bubble point
(C) Superheated vapour
(D) Partially vapour
GATE
2011
Answer: (D)
A gas mixture is in contact with a
liquid. Component P in the gas mixture is highly soluble in the liquid.
Possible concentration profiles during absorption of P are shown in the
choices, where
x: mole fraction of P in bulk liquid
y: mole fraction of P in bulk gas
xi: mole fraction of P at the
interface in liquid
yi: mole fraction of P at the
interface in gas
y*: equilibrium gas phase mole fraction
corresponding to xi
The CORRECT profile is
GATE
2011
Answer: (A)
Ammonia (component 1) is evaporating
from a partially filled bottle into surrounding air (component 2). The liquid
level in the bottle and the concentration of ammonia at the top of the bottle
are maintained constant. Ni is the molar flux relative to a fixed
location in space and Ji is the molar flux with respect to the
average molar velocity of the constituent species in the gas phase. Assume that
air in the bottle is stagnant. Which ONE of the following is CORRECT?
(A)
N1 = constant, N2
= 0, J1 +J2 = 0
(B)
N1 + N2 = 0, J1
+J2 = 0
(C)
N1 + N2 = 0, J1
= constant, J2 = 0
(D)
N1 = constant, N2
= 0, J1 = constant, J2 = 0
GATE
2011
Answer: (A)
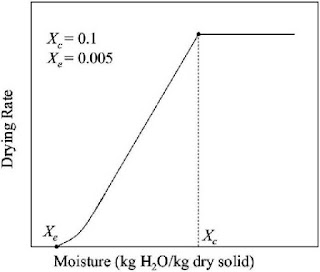
A batch of 120 kg wet solid has initial
moisture content of 0.2 kg water/kg dry solid. The exposed area for drying is
0.05 m2/kg dry solid. The rate of drying follows the curve given
below.
The time required (in hours) for drying
this batch to a moisture content of 0.1 kg water/kg dry solid is
(A)
0.033
(B)
0.43
(C)
0.6
(D)
2.31
GATE
2011
Answer: (D)
Simultaneous heat and mass transfer is
occurring in a fluid flowing over a flat plate. The flow is laminar. The
concentration boundary layer will COINCIDE with the thermal boundary layer,
when
(A)
Sc = Nu
(B)
Sh = Nu
(C)
Sh = Pr
(D)
Sc = Pr
GATE
2011
Answer: (D)
The
flooding velocity in a plate column, operating at 1 atm pressure, is 3 m/s. If
the column is operated at 2 atm pressure, under otherwise identical conditions,
the flooding velocity will be
GATE
2010
Answer: (A)
At
25⁰C
and 90% relative humidity, water evaporates from the surface of a lake at the
rate of 1.0 kg/m2/h. The relative humidity that will lead to an
evaporation rate of 3.0 kg/m2/h, with other conditions remaining the
same, is
(A)
30%
(B)
50%
(C)
60%
(D)
70%
GATE
2010
Answer: (D)
Common Statement for the next two
questions
Water
is used to absorb ammonia from a gas mixture in a single separation stage
contactor. The process is schematically represented in the figure below.
The
molar gas and liquid flow rates, and the inlet mole fractions are given in the
figure. Both the liquid and the gas phases are well mixed, and the equilibrium
relation between y and x is given by y* = x.
If
the stage is ideal, then the value of y is
(A)
1/15
(B)
1/10
(C)
2/1
(D)
1/6
GATE
2010
Answer: (A)
If
the stage efficiency is 50%, then the value of y is
(A)
1/12
(B)
1/6
(C)
¼
(D)
1/3
GATE
2010
Answer: (A)
A liquid flows
over a flat naphthalene plate of length L, at a Reynolds number (ReL
= Lρu∞/μ) of 1500, as shown in the figure. The surface concentration
of naphthalene is CAI > CA∞ and the surface
temperature is TC>T∞. Assume Pr = Sc = 1.
Then
the Nusselt number and the friction coefficient at x= L, are
(A)
10, 1/75
(B)
10, 10
(C)
20, 10
(D)
1/75, 5
GATE
2010
Answer: (A)





No comments:
Post a Comment